Background
As a team we wanted to design and build a self-balancing riderless bike. Our goal was to create two different control systems that would be able to balance the bike under many circumstances. The first control system is designed to run a reaction wheel. the second control system runs a linear actuator to control steering angle. Both of these systems are meant to keep the bike upright without a rider or user input.
Original design goals
-
The project is to make autonomous, self-balancing bicycle using remote communication and control technology.
-
It is a riderless system that will be able to balance itself.
-
A remote control will allow a user to toggle between direct steering and preset functions that will drive the bike.
-
At speed the bike will rely on a control system operating the standard handle bar steering to keep the bicycle balanced.
-
At lower speeds the bicycle will remain upright using a reaction wheel.
-
In both modes a the user will control the forward motion using a joystick.

The main control systems
Reaction Wheel:

A reaction wheel uses the law of conservation of momentum. The Torque applied to to reaction wheel by a motor will have an opposing torque on the bicycle
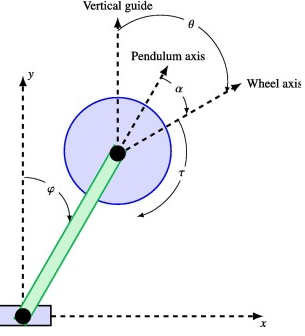
The reaction wheel uses the inverted pendulum model. At all times the reaction wheel is trying to make the angle phi go to zero
Linear Actuator Steering:
The linear actuator will either extend or retract at high speed. This in turn will change the steering angle of the handlebars of the bike.



